Asset
Understand how asset items work in Wikio, including raw media management, publishing, and analytics.
An asset is any media file you upload to Wikio: videos, images, audio files, or documents. Assets are the building blocks of your library—they can be organized into projects, searched with AI, and transformed through workflows.
What counts as an asset#
| Type | Formats |
|---|---|
| Video | MP4, MOV, AVI, MKV, WebM |
| Image | JPG, PNG, GIF, TIFF, WebP |
| Audio | MP3, WAV, AAC, FLAC |
| Document | PDF (for briefs, scripts, guidelines) |
Each uploaded file becomes a distinct asset with its own metadata, tags, and history.
Upload assets#
Open your workspace
Navigate to the workspace or project where you want to add files.Upload
Click Upload or drag files directly into the browser window. You can upload multiple files at once.
Wait for processing
Wikio analyzes each asset—extracting metadata, generating thumbnails, and running AI indexing. Progress appears in the upload panel.
AI indexing#
Once uploaded, Wikio's AI automatically processes each asset:
- Transcription: Spoken words are converted to searchable text.
- Visual analysis: Scenes, objects, and faces are detected and tagged.
- Auto-tagging: Relevant keywords are added based on content.
This indexing lets you search by what's said or shown in a video, not just by filename or manual tags.
Asset details#
Click an asset to open its detail view:
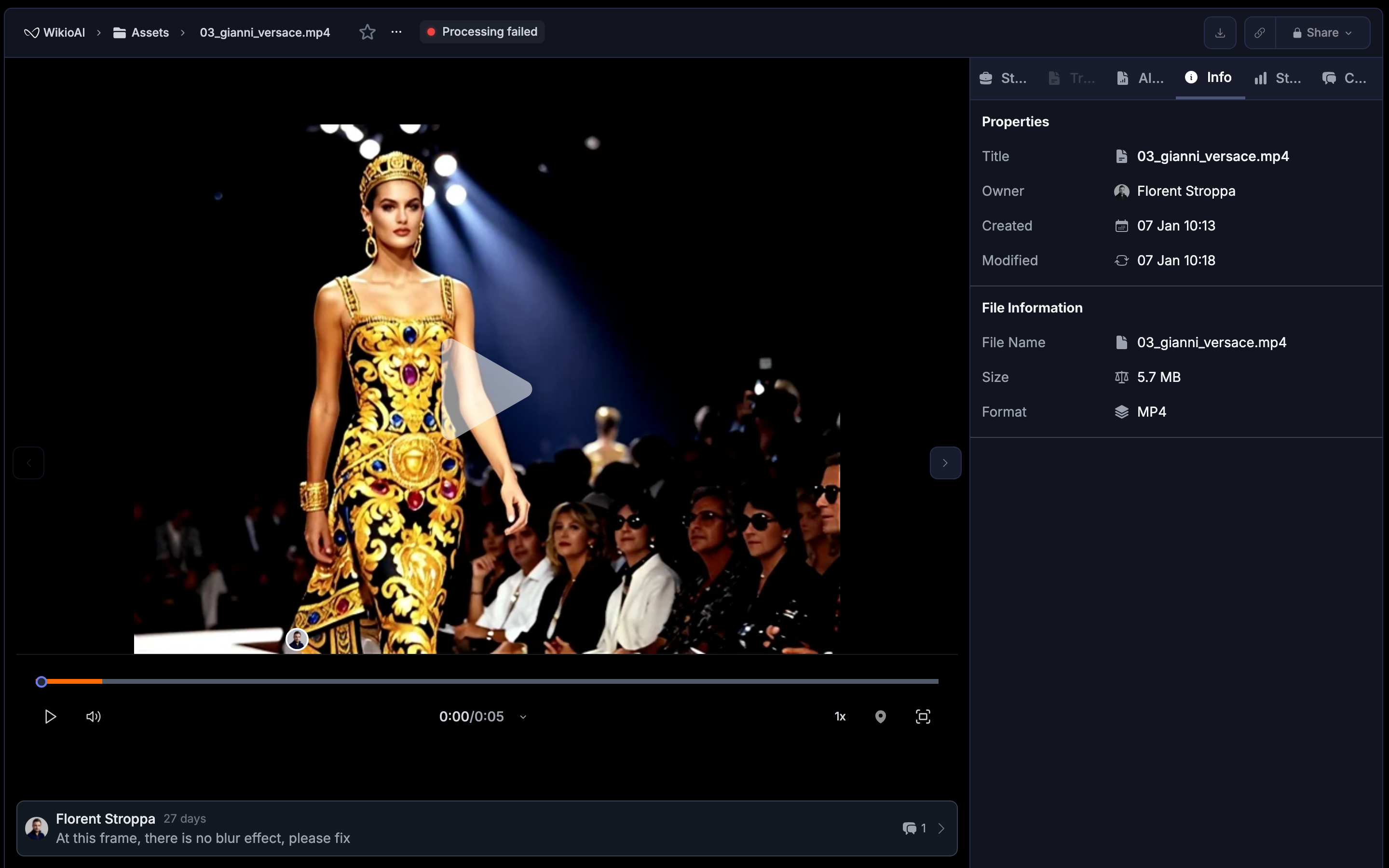
- Preview: Watch video or view images with the built-in player.
- Metadata: See file size, duration, resolution, upload date, and uploader.
- Tags: View auto-generated and manually added tags.
- Transcription: Read the full transcript (for video and audio).
- Activity: Track who viewed, edited, or commented on the asset.
Organize assets#
Tags#
Add custom tags to group related assets:
- Open the asset detail view.
- Click Add tag and enter your label.
- Use tags to filter search results later.
Collections#
Group assets into collections for easy access:
- Create a collection from the sidebar.
- Drag assets into the collection or use the Add to collection menu.
- Collections can be shared with specific teammates or clients.
Projects#
Assign assets to projects to track production progress:
- Raw footage goes into a project as input.
- Versions and edits live alongside the originals.
- The final deliverable becomes the project's Master Release.
Search assets#
Use the search bar to find assets by:
- Keywords: Match tags, titles, or descriptions.
- Spoken words: Find the exact moment someone says a phrase.
- Visual content: Search for scenes containing specific objects or actions.
Filter results by date, file type, project, or tag to narrow down large libraries.
Asset versions#
When you edit or transform an asset, Wikio can create a new version rather than replacing the original:
- Version history: See all iterations of an asset in one place.
- Compare: Toggle between versions to review changes.
- Restore: Roll back to a previous version if needed.
Sharing assets#
Share individual assets or entire collections:
- Click Share on the asset or collection.
- Enter collaborator emails or select teammates.
- Choose permission level: view, comment, edit, or full access.
Shared assets appear in the recipient's Shared with me section.
Analytics#
Track how assets are used:
- Views: See how many times an asset was opened.
- Downloads: Count exports and file downloads.
- Engagement: For shared assets, see viewer activity over time.
Analytics help you understand which content resonates and how your library is being used.
Best practices#
- Name files clearly: Descriptive names make manual searching easier alongside AI search.
- Add context tags: Even with AI tagging, manual labels for campaigns or projects improve organization.
- Archive instead of delete: Move outdated assets to an archive collection rather than deleting—storage is often cheaper than recreating lost work.
- Use projects for production: Keep raw footage and deliverables together in a project to maintain context.